*
Interest of the canine models in hereditary myopathies * Research of therapeutic processes * Development of tools of functional evaluations  |
Development of functional evaluating tools Each evaluation method presented below allows distinguishing significantly healthy dogs and dystrophic dogs. Therefore, these tools are able to highlight the benefits provided by different therapeutic strategies applied to the dystrophic dogs. Qualitative evaluation of the motor abilities
using clinical scores
Quantitative evaluation of the gait quality using accelerometry Muscle characterization by MNR Analysis of the muscular force in vivo In order to track the locomotive evolution of the dogs, we established a grid of clinical scores. 12 locomotive criteria (12 items) are examined (gait, weight transfer, jumping, crossing of an obstacle, etc). For each item, a mark between 0 and 2 is assigned; the zero value corresponding to the normal situation, the value 2 corresponding to the most critical situation. Each animal is evaluated once a month.    Project coordinator: Ines Barthelemy The
accelerometry measurements consist in recording dog accelerations
according to three axes (dorso-ventral, medio-lateral, cranio-caudal).
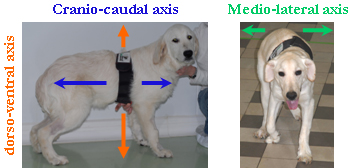 The
accelerometer (Equimetrix device ®) is fixed under the dog
sternum
using an elastic belt. Healthy
and
dystrophic dogs are encouraged to walk as spontaneously as possible
along a
corridor. Accelerations are recorded without interruptions and data are
analyzed
by samples of 10 seconds of stabilized walk. This study is conducted
with the
scientific assistance of Jean Yves Hogrel (
 Examples
of recordings showing the irregular gait of the dystrophic dog.
Project coordinator: Jean Laurent Thibaud In the aim to appreciate objectively and non-invasively the muscle state, MNR analyses are performed in collaboration with the team of the professor Pierre Carlier ( 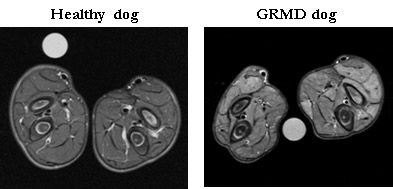 Project coordinator: Ines Barthelemy This examination consists in the measurement of the force generated by the foot flexion and the finger extension following the stimulation of the fibular nerve (under the knee). Six trains of 100 stimulations of 0,1ms at 50Hz are applied with one-minute interval. The absolute tetanic contraction of a leg is given by calculating the average of five tetanic contractions measurements. This value is standardized according to the animal weight in order to compare results obtained for different animals. 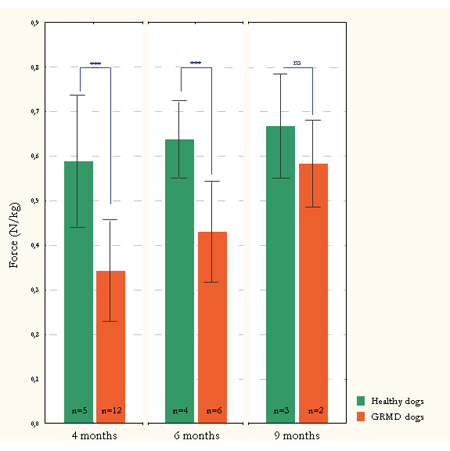 |